Disk erasure pertains to the erasing of data on each of a machine’s disks when the machine has been released (see Release action) back into the pool of available machines. The user can choose from among three erasure types before confirming the Release action. A default erasure configuration can also be set.
Erasure types
The three types of erasure types are:
- Standard erase
- Secure erase
- Quick erase
Each of these are explained below.
Standard erase
Overwrites all data with zeros.
Secure erase
Although effectively equivalent to Standard erase, Secure erase is much faster because the disk’s firmware performs the operation. Because of this, however, some disks may not be able to perform this erasure type (SCSI, SAS, and FC disks in particular).
Quick erase
Same as Standard erase but only targets the first 1 MB and the last 1 MB of each disk. This removes the partition tables and/or superblock from the disk, making data recovery difficult but not impossible.
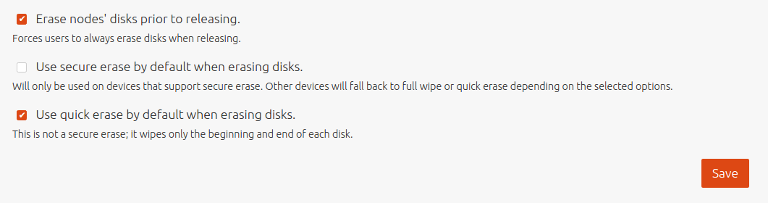
Default configuration
A default erasure configuration can be set on the ‘Settings’ page by selecting the ‘Storage’ tab.
If option ‘Erase machines’ disks prior to releasing’ is chosen then users will be compelled to use disk erasure. That option will be pre-filled in the machine’s view and the user will be unable to remove the option.
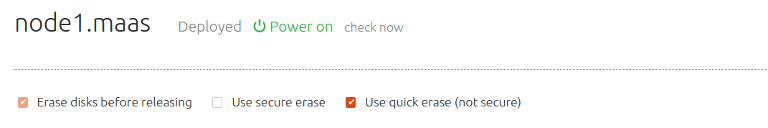
With the above defaults, the machine’s view will look like this when the Release action is chosen:
Where ‘secure erase’ and ‘quick erase’ can then be configured by the user.
Order of preference
If all three options are checked when the machine is released the following order of preference is applied:
- Use ‘secure erase’ if the disk supports it
- If it does not then use ‘quick erase’