The topic of subnet management pertains to whether or not MAAS is in full control of a subnet. When a subnet is managed, MAAS handles all aspects of IP address allocation. This process includes DHCP leases and assigned static addresses. Typically MAAS would have one managed subnet, but any additional subnets can be unmanaged. This arrangement allows for more control over which subnet gets used for DHCP and which ones do not. Additionally, as detailed below, an unmanaged subnet treats reserved IP ranges differently, and in a way that some administrators find more intuitive.
Four questions you may have:
- What are managed subnets?
- What are unmanaged subnets?
- What is IP address tracking?
- How do I control subnet management
Managed subnets
When you enable management for a subnet, MAAS will:
- Lease addresses for DHCP from a reserved dynamic IP range
- Assign static addresses not included in a reserved IP range, typically via ‘Auto assign’ IP allocation mode for a node.
See Concepts and terms for an explanation of the two kinds of reserved IP ranges MAAS uses and Post-commission configuration for information on IP allocation modes.
Unmanaged subnets
When management is disabled for a subnet, the definition of a reserved IP range differs from the managed mode. Here, a reserved IP range tells MAAS to only allocate addresses from this range (via ‘Auto assign’). Also, DHCP will never lease addresses from an unmanaged subnet.
Controlling subnet management
By default, MAAS manages subnets in your configuration, but it is easy to change this.
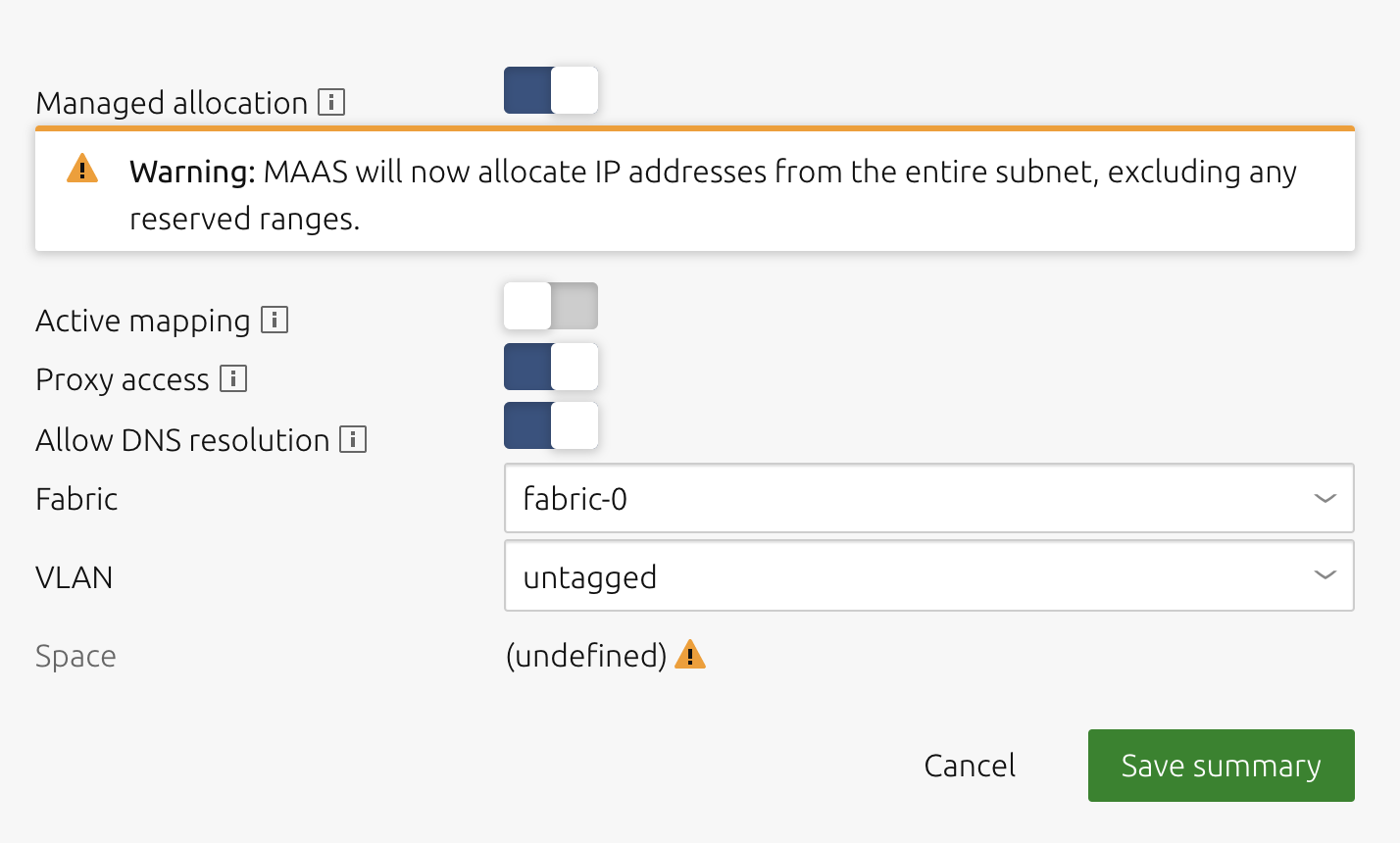
To disable (or re-enable) subnet management navigate to the ‘Subnets’ page and select the subnet. Press the ‘Edit’ button to allow changes. The ‘Managed allocation’ field will become a slide switch. Click the label (or the switch icon itself) to toggle between enabled (dark blue) and disabled (grey) and click ‘Save summary’.
IP address tracking
MAAS will keep track of all assigned addresses, regardless of whether they come from managed or unmanaged subnets.